
The most common degenerative-dystrophic disease of the spine is osteochondrosis. Its peculiarity is that in the initial stages it does not manifest itself in any way, so many patients turn to the doctor when the processes of tissue destruction have already gone far. But even in this case, the diagnosis is not made immediately, but after a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations. It is very important to correctly diagnose osteochondrosis, because the earlier treatment is started, the greater the opportunity to prevent complications. It is for this reason that you need to identify the symptoms of osteochondrosis in time and consult a doctor.
Causes and mechanism of development
Osteochondrosis begins with destructive processes in the intervertebral discs. They gradually dry out and decrease in volume. This leads to the fact that the disks can no longer perform their functions correctly. They can collapse, and then a hernia develops. But most often this condition leads to the development of osteochondrosis.
After all, the intervertebral disc protects the vertebrae from destruction, serves as a shock absorber during various movements and keeps the vertebrae in the correct position. As its volume decreases, the vertebrae become displaced. Instability of a segment of the spine leads to the formation of osteophytes - bone growths that hold the vertebrae at a distance. Otherwise, pinching of nerve roots and compression of blood vessels may occur. All these processes cause the presence of many different signs of osteochondrosis, which is why it is so difficult to diagnose it on time. But if you know why this pathology develops, people at risk can be more careful.
Osteochondrosis is usually caused by the following reasons:
- congenital disorders in the development of the spine or connective tissue defects;
- injuries or constant overload, heavy physical labor;
- poor posture, flat feet, wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time, sedentary lifestyle;
- obesity, poor nutrition, excess weight;
- exposure to chemicals, for example, having bad habits, taking certain medications;
- frequent stress;
- natural processes occurring during the aging of the body;
- constant vibration effect on the spine.
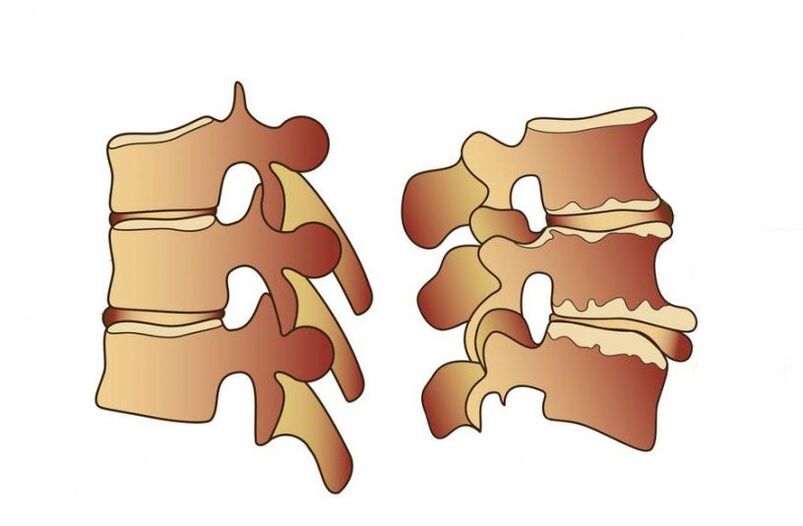
Osteochondrosis develops after a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc, after which the vertebrae themselves begin to collapse
Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health in order to consult a doctor at the first symptoms. This is especially important for athletes, loaders, drivers, gymnasts, women, who often worry about their loved ones and experience stress because of this.
Symptoms
Signs of osteochondrosis depend on the stage of the disease, as well as on which part of the spine is affected by degenerative processes. Very often, at first the patient does not even feel back pain, only slight stiffness in the morning. In the process of destruction of the intervertebral disc due to displacement of the vertebrae, the nerve roots are pinched and pain occurs. Depending on the location of the disease, they can appear not only in the back area. Often the pain radiates to the shoulder blade, chest, arm or leg, and there may be headaches.
A feature of osteochondrosis in the initial stages is also that the pain intensifies with physical activity and subsides after rest. Even after adopting a comfortable body position, the patient feels better. Painful sensations worsen after hypothermia, stress, prolonged stay in a static position, for example, when working at a computer or while sleeping on an uncomfortable bed. Very often, with osteochondrosis, stiffness in movements, muscle weakness, and constant fatigue are observed. The patient tries to take a comfortable position in which he experiences less pain.

The main sign of lumbar osteochondrosis is pain and stiffness in movement.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
The most common location of degenerative-dystrophic processes is the lumbar spine. It can withstand the heaviest loads not only when moving, but also when a person sits for a long time in one position. Due to the sedentary lifestyle of modern people, the muscular corset here is weak, so any overload can lead to the destruction of discs or displacement of the vertebrae.
In addition to pain and general stiffness, there are special symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis in the lumbar region. If the following signs make themselves felt every now and then, you need to make an appointment with a neurologist:
- lower limbs go numb;
- skin sensitivity is impaired, paresis may develop;
- pain is felt in the pelvic organs, their functioning is disrupted;
- the patient cannot turn or bend, pain is felt even when sitting.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
It is especially important to know what symptoms the patient experiences with cervical osteochondrosis. After all, sometimes pain in the neck is not even felt, and other symptoms are similar to vascular disorders that a person is trying to treat with medications. If the destructive processes in the cervical spine are not stopped, this can lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain and even complete paralysis of the body.
Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the following signs in time:
- headaches that cannot be relieved with conventional analgesics;
- dizziness occurs when turning the head;
- pain can be felt in the shoulders, back of the head, arms;
- vision deteriorates, spots or colored spots are visible before the eyes;
- there is hearing loss, tinnitus;
- tongue and fingers go numb;
- coordination of movements is impaired.

With cervical osteochondrosis, headaches and tinnitus are often observed
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
Signs of osteochondrosis in the thoracic region are easily confused with diseases of the internal organs. And although the main symptom is back pain, it has its own characteristics. Patients describe this feeling as if the chest was being squeezed by a hoop. The pain intensifies when inhaling and exhaling, so many attribute these sensations to heart pathologies.
With thoracic osteochondrosis, the pain will intensify with hypothermia, raising your arms up, and also at night. You may experience numbness of the skin, goosebumps, and coldness of the extremities. Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system often occur.
Diagnostics
To prevent complications of osteochondrosis, it is very important to consult a doctor as soon as its first signs appear. This is stiffness in movement and back pain after exercise. This pathology is treated by a vertebrologist or neurologist. An experienced doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis during an examination and conversation with the patient.
But some symptoms of the disease are very nonspecific and resemble manifestations of many other pathologies. Therefore, differential diagnosis is very important, which will help exclude diseases in which vascular and neurological symptoms also develop. This may be angina pectoris, hypertension, peptic ulcer, pyelonephritis. The main difference between osteochondrosis and them is that it has a chronic course and develops slowly, with periodic exacerbations, and pain most often subsides with rest.
But without special diagnostics, it is still difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Most often, instrumental examination methods are used for this: radiography, CT, MRI, ultrasound, myelography and others. Sometimes laboratory tests may also be needed. They will help identify the presence of an inflammatory process and an increase in the concentration of calcium in the blood.
The most common diagnostic method at the initial stage of the disease is radiography.
Radiography
At the initial stage, X-ray diagnostics are required to confirm the diagnosis. This is the main method of examination for osteochondrosis. It is the simplest and most accessible, and has the fewest side effects. After determining the location of the pain, photographs of this area of the spine are taken. They are usually carried out in two projections: direct and lateral.
If the diagnosis is made correctly, this will be indicated by the following radiological signs: the distance between the vertebrae is reduced, atrophy of the intervertebral discs is observed, osteophytes are visible, there may be destruction of vertebral tissue or a change in the shape of the spinal column.
Myelography
This is a more complex method, may have side effects, and is not suitable for everyone. After all, myelography is based on the injection of a special contrast fluid into the spinal canal. This may cause an allergic reaction or even damage to the spinal cord. After this, the spine is x-rayed.
This method allows you to examine the spinal canal and determine where it is damaged by degenerative processes. In addition, myelography can determine the presence of intervertebral hernias at the initial stage.

MRI is a more informative examination method, so it is used when differential diagnosis is necessary.
Tomography
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis using CT or MRI is carried out less frequently, since these methods are not yet available everywhere. Therefore, they are used in difficult cases, as well as if it is necessary to differentiate osteochondrosis from other diseases. But with an MRI or CT scan, you can examine the spine and surrounding tissues in great detail.
These diagnostic methods allow you to see the condition of the blood vessels, the presence of hernias, compression of the nerve roots, and the shape of the intervertebral discs. They are necessary for the differential diagnosis of osteochondrosis from osteomyelitis, spinal cord tumors, spondylitis, ankylosing spondylitis, and syringomyelia.
Timely identification of symptoms of osteochondrosis and its correct diagnosis will help to begin treatment on time. This will prevent the development of complications, alleviate the patient’s condition and reduce the number of exacerbations.
















































